Main performance characteristics of commonly used fibers
Commonly usedMain performance characteristics of fibers
1. Raw cotton: There are two main varieties of cotton fiber
Long-staple cotton (also known as island cotton): The fiber is long and thin, with a length of 33~64mm, linear density: 1.2~1.4dtex, good fiber quality, suitable for spinning high-count yarns and weaving high-end fabrics. Egypt, Sudan, Morocco and Xinjiang, Guangxi and Yunnan in my country are the main producing areas.
Fine velvet cotton (upland cotton): fiber length 23~33mm, linear density: 1.5~2dtex. About 98% of the cotton grown in my country is fine-staple cotton.
The structure and performance of raw cotton: There is a cavity in the middle and a natural twist in the longitudinal direction. It is a slender flat belt-shaped hollow object with natural twist. The main chemical component is fiber. Because the molecule itself has many hydrophilic genes and is a porous material, it has good hygroscopicity and air permeability. Cotton fabrics are comfortable to wear, breathable, and have good wearability.
The main component of cotton fiber is cellulose, so cotton fiber is resistant to alkali and not acid. This characteristic allows cotton yarn and fabrics to swell and naturally twist and stretch under the action of dilute alkali (such as 18% NaoH solution). Straight, giving the cotton fabric a silky luster. This treatment is called “mercerization”, and the cotton fiber also has high strength.
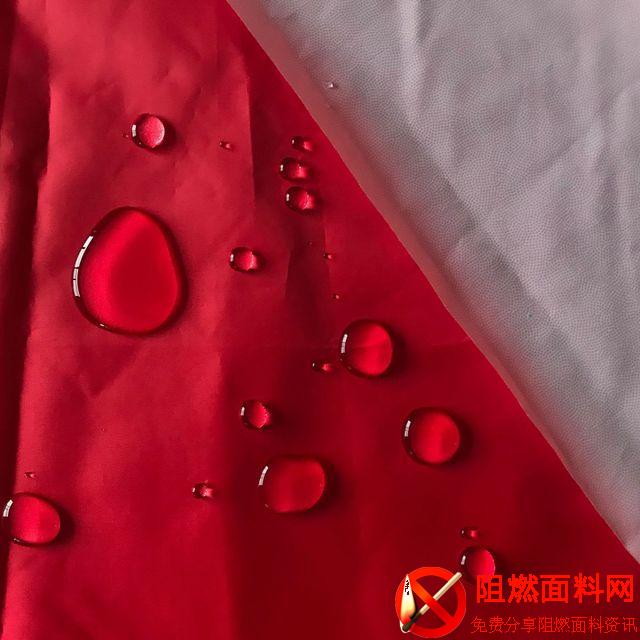

The disadvantage is that cotton fiber has poor elasticity, and cotton fabrics are prone to wrinkles and deformation. In order to improve the stiffness and shape retention of cotton fabrics, the fabric can be anti-wrinkle, non-iron finishing, or blended with cotton fiber and other fibers to improve the shape retention of the fabric.
2. Hemp: There are many types of hemp fiber, among which the two main types that are soft in texture and can be used as textile fibers are ramie and flax:
Structure and performance: It has a central cavity, horizontal stripes on the longitudinal surface, and no bends.
Ramie has a waist-shaped cross section, while flax has a polygonal shape with a smaller middle cavity. Ramie fiber length is the longest among plant fibers, and its strength is the largest among natural fibers, equivalent to 8 to 9 times that of cotton fiber, and it is wet when wet. The strength is greater than the dry strength. The hollow structure of hemp fiber and its main content are cellulose, which makes it have good hygroscopicity and moisture dissipation, and its thermal conductivity is fast.
Therefore, linen fabrics are comfortable, cool, and sweat-removing in summer. In addition to cellulose, linen fibers also contain lignin, so they feel rough and hard. They are rarely used as underwear. Linen fabrics have an inhibitory effect on a variety of germs and molds. , with antibacterial, anti-mildew and deodorizing functions. However, linen fiber is the least elastic among natural fibers. Linen fabrics wrinkle easily and must be ironed after washing to make them smooth and crisp.
3. Wool: There are many types of wool fibers, and sheep wool is the most commonly used in textiles.
Due to different sheep breeds, origins and wool growth parts, the quality varies greatly. Among them, Australian Merino sheep have the best quality in the world and are also the sheep species with the highest wool yield. Merino wool is of average length. It is 55~75mm, and the linear density (thickness) is 3.4~7.6dtex.
Morphological structure and performance: The longitudinal direction is cylindrical (or elliptical) covered with scales, with natural curls, and the cross-section is approximately circular. The scale layer has the function of protecting wool fibers. The density and degree of attachment of the scales have an impact on the luster of the wool. The influence is large. The cortical layer within the scale layer determines the physical and chemical properties of wool. Since the scales are arranged in a directional manner, friction along the scales has a small friction factor. The scales open under hot and humid conditions, and the wool fibers are repeatedly squeezed and rubbed by mechanical external forces. ;
Due to the difference in friction coefficient, the movement of the fibers is directional. Each fiber carries the fibers entangled with it and slowly wriggles in a certain direction. The entanglement and winding of each other causes the wool fiber scales to interlock with each other to form a felt. Finally, the wool fabric This phenomenon of shortening and thickening is the unique milling property of wool. The milled wool fabric is rich and soft, making it an ideal fabric in winter. However, this characteristic of wool fiber makes its dimensional stability poor, so Daxin wool fabrics should not be machine washed (should be dry cleaned). Wool fabrics on the market marked “machine washable” have been specially treated to destroy scales.
Wool has excellent moisture absorption properties, and the maximum moisture absorption capacity of fine wool can reach 40%. Wool fabrics usually give people a dry feeling. Wool fibers have good elongation and elastic recovery capabilities, so the fabric has good elasticity, feels fluffy, soft, smooth and waxy, has a soft luster, is stiff and has good moisturizing properties. The main chemical component of wool is protein, so wool fiber is acid-resistant and not salt-resistant, so it should be washed with neutral or acidic detergents. In addition, the fineness of wool fibers is low.
4. Silk: There are two commonly used types: mulberry silk and tussah silk.
Silk is composed of two silk fibroin and sericin covering the outside. The cross-section is a relatively irregular triangle, and the longitudinal direction is relatively straight and smooth. The fineness of a single silk is 2.2~4.4dtex, and the strength is similar to cotton fiber. Because With the triangular cross-section of silk fibroin, silk has a soft luster that other fibers cannot match, and its specific gravity is small, so its fabric is light, elegant and smooth to the touch.
Silk absorbs and dissipates moisture quickly and feels very cool when worn in summer. Silk is a protein fiber, so it is similar to wool and has the characteristics of acid and alkali resistance.The elasticity is also poor and starts to shrink above 100℃.
5. Spandex: It is a highly elastic fiber
The international trade name is Spandex. This fiber was born in 1959 by DuPont in the United States and named Lycra. The elasticity of spandex is higher than other fibers, with large deformation ability and good elastic recovery performance. The recovery rate reaches 90% when elongated to 500%, and can be dyed into various colors.
It feels smooth, has low hygroscopicity, has lower strength than ordinary fibers, is light and soft, and has good acid, alkali and light resistance. Bare silk is rarely used directly, and spandex is often used as the core, and it is used with cotton, wool, silk, Polyester, nylon, etc. are imitated into core-spun yarns and wrapped yarns and woven into elastic fabrics, making the fabrics soft, comfortable and fit-fitting, and stretch freely. They are widely used. As long as the fabrics contain a small amount of spandex (3%~5%), It can significantly improve the elastic recovery ability of the fabric.

6. Vinyl:
It is less used in clothing and more used in industry. The appearance and feel of the fabric are like cotton, and its elasticity is not as good as polyester and other synthetic fibers. The fabric wrinkles easily and has poor dyeing performance, but its moisture content is worse than other synthetic fibers and its specific gravity is It has a small thermal conductivity, is light and warm to wear, has good strength and wear resistance, and has excellent resistance to chemicals, sunlight, and seawater.
4. New fiber
1. Natural colored cotton is naturally grown non-white cotton. my country began to introduce and plant colored cotton in 1994. Currently, it has brown, green, purple, gray, orange and other color varieties. It is usually used with white cotton and synthetic fibers. Blended without dyeing in the post-process, it is a truly environmentally friendly green fiber. Its length and strength are slightly inferior to white cotton.
2. Removing scales and anti-shrinking wool. The scales of wool give wool shrinkage, which brings many problems to washing and use. Therefore, peeling off and destroying wool scales is the most direct and fundamental anti-shrinking method. After chlorine treatment, The chemical treatment and wool not only obtain a permanent anti-shrinking effect, but also make the wool fiber finer, the fiber surface becomes smooth and shiny, dyeing becomes easier, the product is softer, smoother, and has anti-pilling properties. Features such as machine washability and no itch, give wool fabrics better quality and a wider range of applications. This treatment method is called “wool surface denaturation treatment”, and some people also call it “wool mercerization treatment”.
3. New green cellulose fiber – Lyocell (Lyocell) This is a new type of cellulose fiber developed abroad in the 1990s. It is an artificial fiber that is regenerated by spinning natural cellulose raw materials directly into an aqueous solution of NMMO. The production process of cellulose fiber is simpler than that of viscose. The solvent used is non-toxic and no harmful substances are released. The solvent recovery rate reaches 99.7%. The product waste can be biodegraded after 5 to 6 weeks in the soil and does not cause environmental pollution. It is called cellulose fiber. It is the green fiber of the 21st century. It provides a direction for the environmentally friendly production of cellulose fibers and product upgrading.
At present, the British company Courtaulds and the Austrian company Lenzjng are the main manufacturers. Our country often quotes the British trade name (Jencel), which is translated as Tanser or Tencel. Lyocell fiber combines the advantages of natural fibers and synthetic fibers. It has the advantages of good hygroscopicity, breathability, and comfort of cellulose fiber. Its wearing comfort is much better than that of polyester. It has beautiful luster, soft hand feel, good drape, and good elegance. At the same time, it has the advantage of high strength of synthetic fibers. Its strength is higher than cotton and ordinary viscose. It has good dimensional stability in washing and good cost performance. It has good blending performance and can be blended with other natural fibers and synthetic fibers.
The following table compares the performance of Lyocell fiber with other fibers. Fiber properties Lyocell Ordinary viscose Modal cotton Polyester Dry strength CN·tex42~4820~2534~3825~3048~60 Wet strength CN·tex26~3610~1518~2226~3246~58 Dry breaking elongation %10~1518~2314 ~168~1025~30 Wet elongation at break %10~1822~2815~1812~1425~30 Wet initial modulus CN·tex (elongation 15%) 250~27040~50180~250100~150210 Moisture regain 11~13% 13%12%8.5%0.4%
4. Microfiber products have a soft, delicate, smooth feel and soft luster. Microfiber has a large specific surface area and strong surface adsorption. It has high cleaning ability and can be used as highly absorbent materials (such as towels and paper towels). Microfiber can be used to make silk-like fabrics, high-density waterproof and breathable fabrics, peach skin fabrics, deerskin-like fabrics, etc. At present, there is no unified standard for the classification of ultrafine fibers in the country, but generally, the fineness is 0.55~1.4dtex (0.5~1.3 denier) as fine denier yarn, and the fineness is 0.33~0.55dtex as ultra-fine denier yarn. The 0.11~0.33dtex is extremely fine denier.
5. Cool fiber (Coolmax) DuPont’s Dacron has a four-groove cross-section, which increases the liquid water conduction area and has excellent moisture treatment functions (breathable and moisture-permeable). It quickly delivers moisture to the fabric like a pipe. The outer layer enhances the wearer’s comfort and also has excellent dyeability and stain resistance. It is suitable for men’s and women’s shirts, outdoor and sportswear fabrics, making the wearer dry and comfortable for a long time.
6. Flame retardant fiber The flame retardancy of fiber is generally expressed by the limiting oxygen index (LOI, which is the percentage of the lowest oxygen content that can maintain combustion). The oxygen content in the air is approximately 21%. If the LOI value of the fiber is greater than 21%, it cannot continue to burn in the air after leaving the flame. Generally, fibers with an LOI greater than 26% can be considered flame retardant fibers. Flame-retardant acrylic fiber is the main fiber variety used in the production of flame-retardant fabrics in my country.
The LOI value is above 26%, has good flame retardancy, good dimensional stability, sunlight resistance similar to acrylic, comfortable hand feel, good drape, good resilience, easy dyeing, and good color fastness. In addition, aromatic rings or aromatic heterocyclic rings are introduced into the macromolecular chains of fiber-forming polymers to increase the rigidity of the molecular chains, the density and cohesion of macromolecules, thereby improving thermal stability. For example, aramid 1313 (Nomex) is also a flame-retardant fiber with good flame retardancy.
At 21%, after leaving the flame, it cannot continue to burn in the air. Generally, fibers with an LOI greater than 26% can be considered flame retardant fibers. Flame-retardant acrylic fiber is the main fiber variety used in the production of flame-retardant fabrics in my country.
The LOI value is above 26%, has good flame retardancy, good dimensional stability, sunlight resistance similar to acrylic, comfortable hand feel, good drape, good resilience, easy dyeing, and good color fastness. In addition, aromatic rings or aromatic heterocyclic rings are introduced into the macromolecular chains of fiber-forming polymers to increase the rigidity of the molecular chains, the density and cohesion of macromolecules, thereby improving thermal stability. For example, aramid 1313 (Nomex) is also a flame-retardant fiber with good flame retardancy.