How to choose fireproof cloth to block welding slag and prevent welding sparks, and how much does it cost?
When we purchase fireproof cloth, we should choose it according to our specific needs
1. If it is used vertically and the performance is lower, you can choose fiberglass plastic-coated three-proof cloth. Glass fiber is a flame-retardant material and will not burn. However, the surface coating is made of PVC plastic and can only reach Class B flame retardancy. Advantages: Cheap price
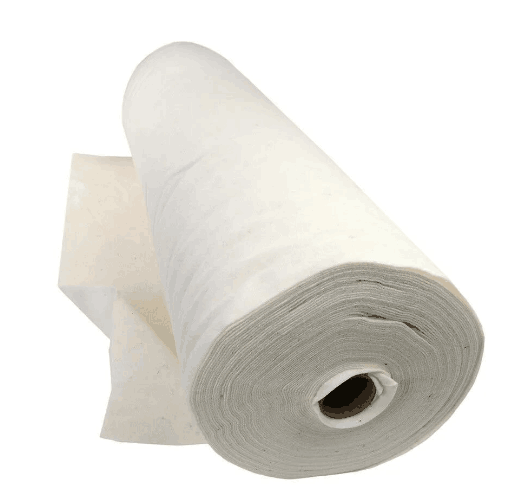

2. If the welding slag is caught laterally, it is necessary to purchase Class A flame retardant fireproof cloth. Since the temperature of the newly dropped welding slag is still very good, using Class B flame retardant cloth will cause smoke or even fire. If our fireproof cloth is used overhead, you can choose Class A flame retardant titanium silicon fireproof cloth, silicon titanium fireproof cloth It is a high-temperature resistant inorganic fiber with a silica (SiO2) content higher than 96% and a softening point close to 1700°C. It can be used for a long time at 900°C and can work for 10 minutes at 1450°C. Works for 15 seconds and still remains intact. Advantages: Good fire protection effect and affordable price
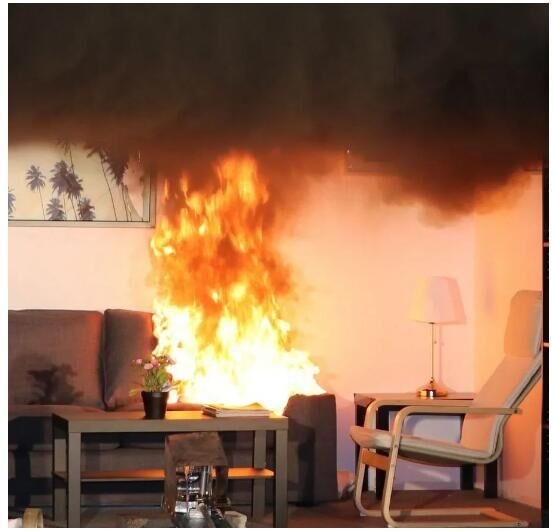

3. If there are items that may be hot under the welding construction, we should purchase dust-free asbestos cloth or ceramic fiber sintered cloth with fireproof and heat-insulating effect. Dust-free asbestos cloth is made of high-quality dust-free asbestos threads interwoven in plain or twill weave. Dust-free asbestos thread is made of asbestos wool as raw material, adding chemical penetrants, soaking and stirring, so that the asbestos wool and chemicals are highly dissolved, divided into very fine fibers, and formed into porridge, and then chemical fixing agents are added. The forming and spinning machine is used to produce the wire, and then the dust-free asbestos wire is made by spinning, drying and other processes. It has the characteristics of stable performance, low conductivity, acid and alkali resistance, etc. It is a very good medium and low temperature refractory insulation material. The heat-resistant temperature can reach 400℃-550℃. It is suitable for various thermal equipment to be used as heat preservation, heat insulation material or processed into other asbestos products.
Ceramic fiber sintered cloth is a fire-proof and heat-insulating cloth made of ceramic fiber cloth that has been deeply processed to evaporate organic matter naturally, so that it does not discolor or emit black smoke when used in demanding environments
Fires that begin in upholstered furniture such as sofas are the leading cause of home fire deaths in the United States, killing approximately 600 people each year. They are not as frequent as cooking fires, but they are about 14 times more likely to cause death than other home fires. Independent of the ignition source, most furniture fire deaths are due to flaming fires, usually following the transition from smoldering to burning. Unfortunately, there are no regulations in the United States that limit the flammability of furniture. This is partly due to the public outcry against chemical flame retardants, which have been used to reduce the flammability of upholstered furniture. Certain types of flame retardants have been shown to have possible adverse effects on human health and the environment. As a result, several U.S. states have introduced regulations restricting the use of flame retardants in furniture.
To prevent furniture fires, fire retardant fabrics are a different technology, viz. They are not based on chemicals or nanoparticles. Instead, as the name suggests, they are fabrics, often fire-resistant fibers in nature, specifically designed to protect flammable filling materials in upholstered furniture. In the event of a fire, these fabrics will reduce the rate at which the filling material burns. The most intriguing thing about fire barriers is that they can use physical means instead of chemicals to reduce fire hazards and meet certain fire performance requirements. They act as a thermal barrier by reducing the amount of heat reaching the liner material and as a mass barrier by slowing the release of flammable liquid and gaseous products produced by the liner when it reaches high temperatures.
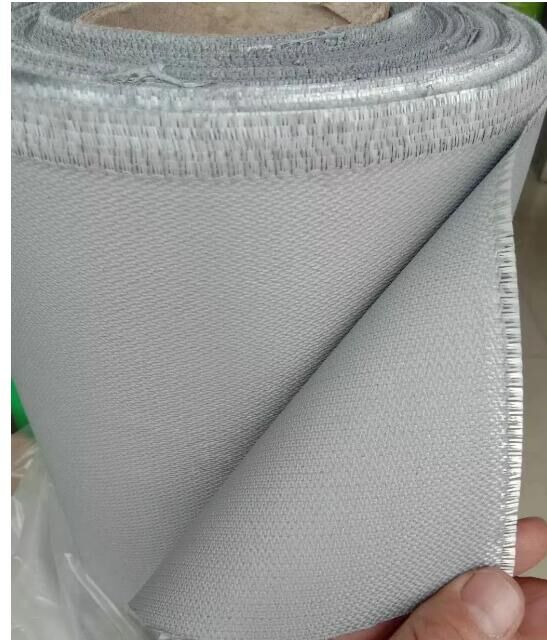

The adoption of a fire barrier approach has proven successful by the mattress industry, which uses fire-resistant fabrics to comply with the 2007 Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) mattress flammability standard. The standard requires mattresses to have a maximum heat release rate (a measure of burning rate) of less than 200 kilowatts (comparable to the heat rate of a burning trash bag filled with newspapers). Performance benchmarks are derived from NIST test methods and analysis, concluding that reducing the range of heat release rates of mattresses will result in measurable and significant reductions in fatalities. As shown in a recent NIST publication, the introduction of this regulation resulted in an approximately 70 percent reduction in fire fatalities. This percentage correlates to 50 to 80 percent of mattresses being replaced and meeting CPSC standards. This is a strong indication that the regulation is very effective.
Comprehensive experiments were carried out in well-appointed rooms, demonstrating the ability of fire barriers to slow the spread of fire, particularly flashover, the moment when almost the entire room catches fire at the same time. Delayed flashover is important because approximately two-thirds of fire deaths occur in fires that achieve flashover. A furniture fire without a barrier (fireproof cloth) takes less than 7 minutes to reach flashover. Barrier-coated furniture ignites more slowly, with flashover times exceeding 20 minutes.

These results can be put into context by comparing flashover time to total first responder response time. Only by intervening before flashover occurs can firefighters prevent flashover and rescue potential fire victims. According to National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards, the target response time for first responders is approximately 13 to 19 minutes.Varies over time, depending on region (urban, suburban or rural). Therefore, first responders may only be able to intervene before flashover if a fire barrier (fireproof cloth) is used.